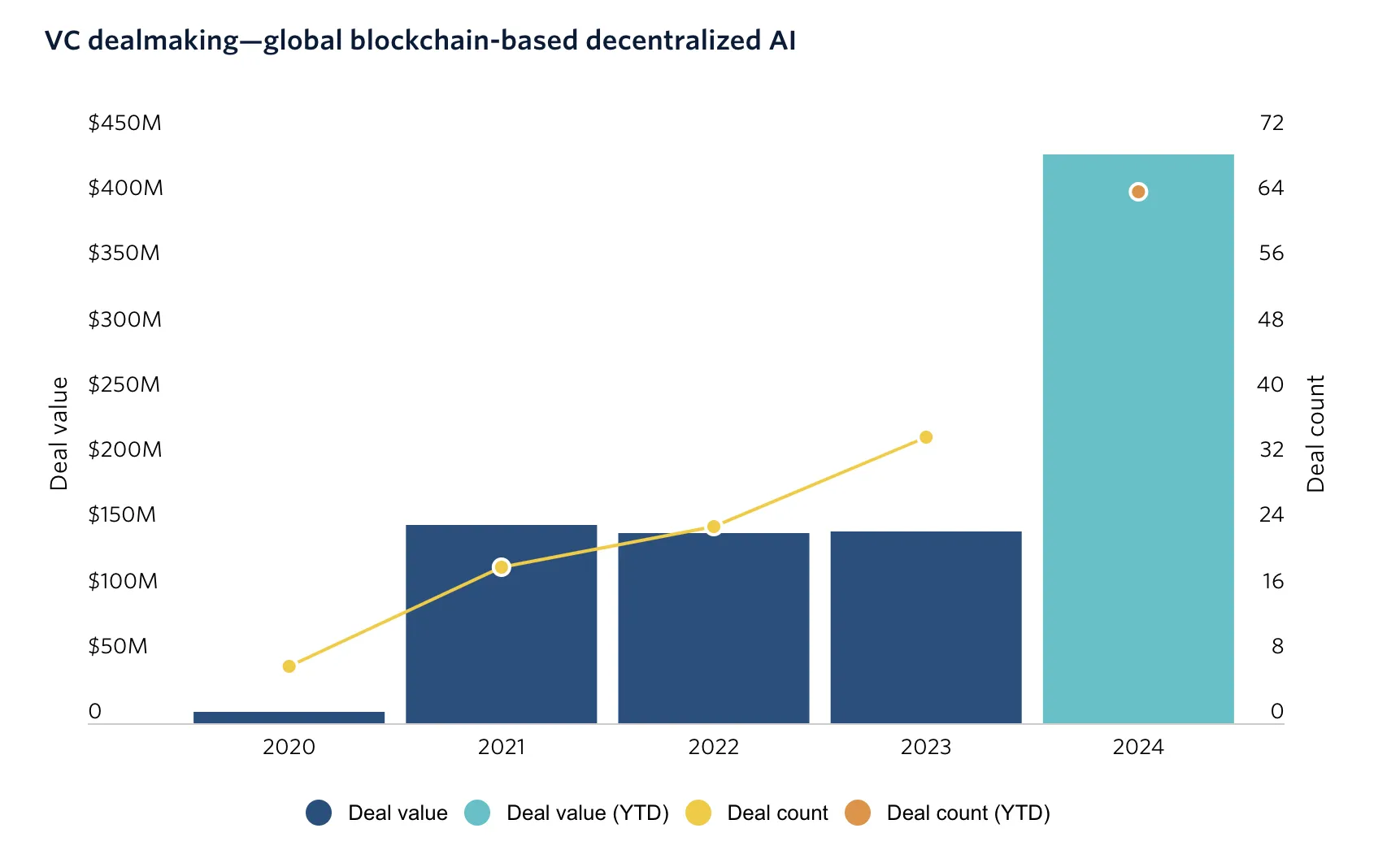
2024 sees unprecedented growth in the decentralized AI sector. According to PitchBook, investors have pumped $436 million into the sector, marking an increase of nearly 200% compared to 2023.
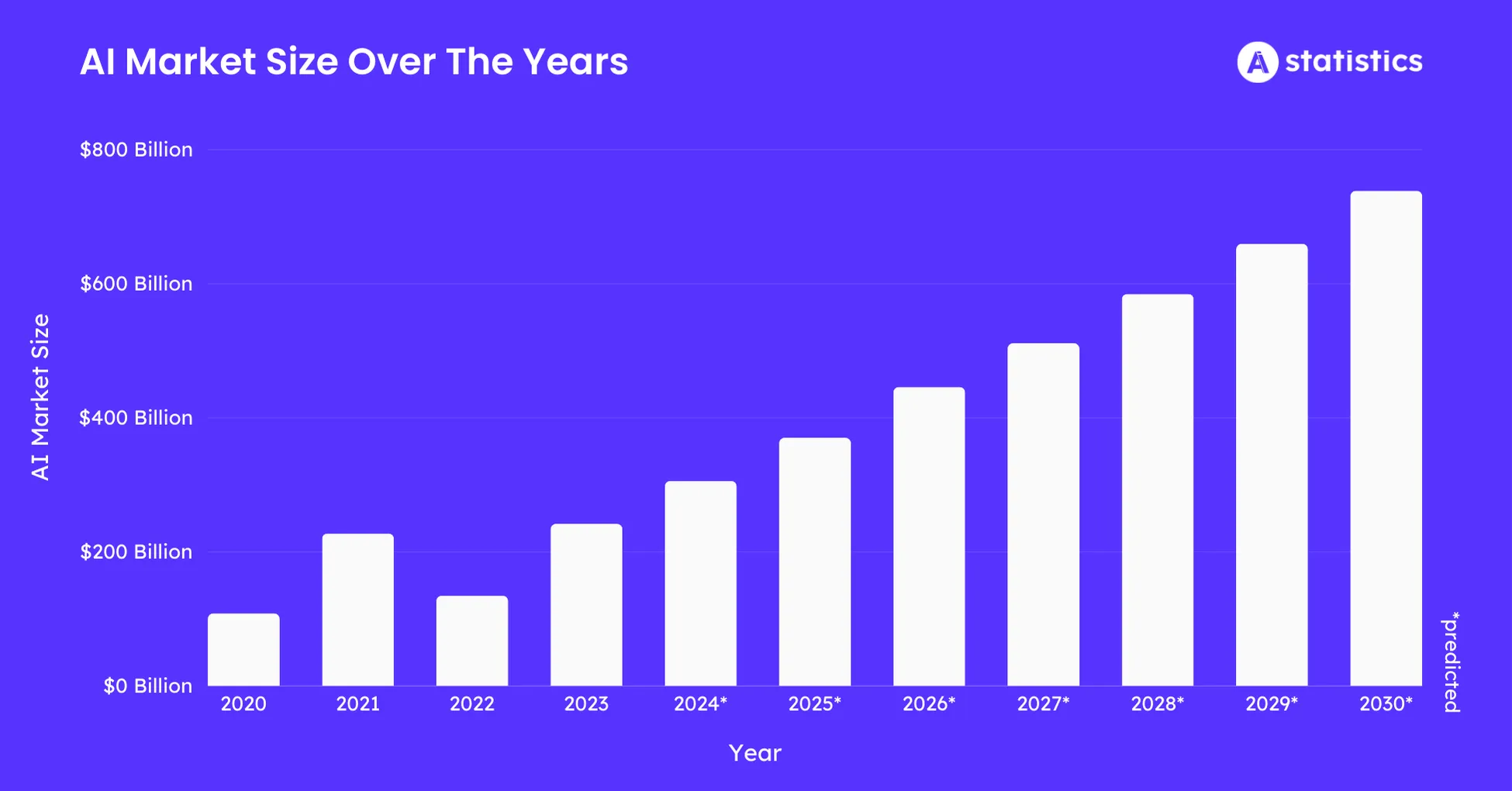
This boom coincides with the impressive market value of the global AI market reaching $214 billion this year. The convergence between AI and blockchain is reshaping how these technologies are developed, accessed, and deployed. However, is decentralized AI more than a speculative trend?
Decentralized AI Analysis
Decentralized AI integrates artificial intelligence into systems that prioritize distributed ownership, governance, and collaboration. Unlike traditional AI models, which are often centralized, decentralized AI operates through trustless frameworks.
Investors are jumping on this trend more than ever, with decentralized AI startups raising more capital this year than the previous three years combined.
Projects like SingularityNET are prime examples of this model, allowing the creation, sharing and monetization of AI services. In March 2024, SingularityNET, Fetch.ai, and Ocean Protocol announced their Token consolidation plan.
This merger aims to advance collaborative AI initiatives and democratize access to these technologies. These frameworks can help reduce dependence on centralized organizations, paving the way for open and fair AI ecosystems.
The rise of decentralized AI is stimulated by its potential to solve problems of privacy and ownership. These agents can manage wallets, conduct transactions, and personalize content while protecting user data.
“Cryptocurrency users already have a strong attachment to owning their assets and data, so decentralized AI is a perfect fit because it allows AI agents to work directly for each person use. What’s even more interesting is that, in Cryptocurrency, you can have joint ownership of these AI agents. Imagine a DAO collectively owning an AI that manages its treasury, or a group sponsoring an AI artist to create unique NFTs. This is about combining the intelligence of AI with the transparency and fairness of blockchain,” Jawad Ashraf, CEO of Vanar, said in an interview with TinTucBitcoin.
Another important driver is the seamless integration between blockchain and AI. Blockchain provides secure data storage, while AI processes the data and generates insights. Community initiatives and the appeal of shared ownership further accelerate adoption.
Challenges and Risks in Decentralized AI
Although promising, decentralized AI is facing major challenges. Scalability remains a technical barrier as blockchain’s current infrastructure struggles to effectively handle AI’s high resource demands.
Trust and governance are also challenges. Transparency and accountability mechanisms are needed to foster this trust.
“Scaling large data and models across decentralized networks without compromising performance is a major obstacle,” Chi Zhang, CEO of Kite AI, said in an interview with TinTucBitcoin.
Data privacy concerns further complicate adoption. A recent Informatica survey found that 40% of data leaders identify Data privacy and protection are major challenges in applying generative AI. Frameworks must address these issues to gain widespread trust from users.
“In theory, one of the most difficult issues is trust. Decentralized AI requires people to trust not only the AI but also the entire network that operates it, which means frameworks need to have clear and transparent mechanisms for governance and decision-making. ,” Ashraf explains.
Decentralized AI must prove useful to overcome the boundaries of retail speculation. For example, privacy-preserving AI can securely analyze sensitive medical data without centralization.
Financial markets provide another practical example. Mark Stokic, Head of AI at Oasis Protocol, highlighted the role of privacy-preserving AI agents in generating trading signals. These agents protect sensitive data while contributing to collective intelligence. The key, he says, is to build something that’s still valuable when the craze cools.
Moving Toward The Future
Forbes predictions show that the global AI market will reaching 1,339 billion USD by 2030a staggering increase from this year’s $214 billion. This development highlights the opportunity for decentralized systems to scale alongside traditional AI.
Stokic envisions these technologies transforming smart cities, financial instruments, and collaborative networks. These use cases can transform industries by prioritizing privacy, efficiency, and user ownership.
“This is not just a theory. We are seeing real-world applications where decentralized networks provide computing power that is otherwise inaccessible. Additionally, we are finally attracting some attention from outside the Crypto world. We are seeing someone with a PhD in AI being the founder of Cryptocurrency companies. It’s not just crypto natives trying to jump on the AI bandwagon, but AI experts who recognize blockchain’s potential to solve fundamental problems in the field,” Stokic said in an interview. with TinTucBitcoin.
To realize its potential, decentralized AI must prioritize real-world applications and sustainable infrastructure. Projects like OG Labs and Warden Protocol are paving the way, showing what can happen when adoption outweighs the hype.
“Decentralized AI must prioritize equitable development by Tokenizing data and model contributions to encourage broad participation while reducing dependence on centralized actors. Real-world use cases, such as implementing DeFi strategies, decentralized supply chain management, and privacy-preserving medical diagnostics, could demonstrate its practical usefulness. Developing interoperable frameworks that enable seamless AI operations across multiple blockchains is essential to develop widespread availability and adoption,” said David Pinger, CEO of Warden Protocol, in an interview with TinTucBitcoin.
Decentralized AI is at a formative moment. The rapid and promising growth faces significant challenges. It represents both a speculative trend and a transformative technology.
Its growth is driven by privacy, transparency and collaborative initiatives. The real test for the field is whether it can deliver practical and transformative applications.
