Hacks and fraud in the Cryptocurrency sector have resulted in losses of more than $2.3 billion this year, highlighting the persistent nature of security vulnerabilities in the industry. This number spans over 165 incidents, marking a 40% increase over the previous year.
While the overall figure is lower than the $3.7 billion lost in 2022, the continued rise in attacks shows that industry defenses remain inadequate to deal with threats advanced.
Ethereum and Access Control Bugs Dominate Losses
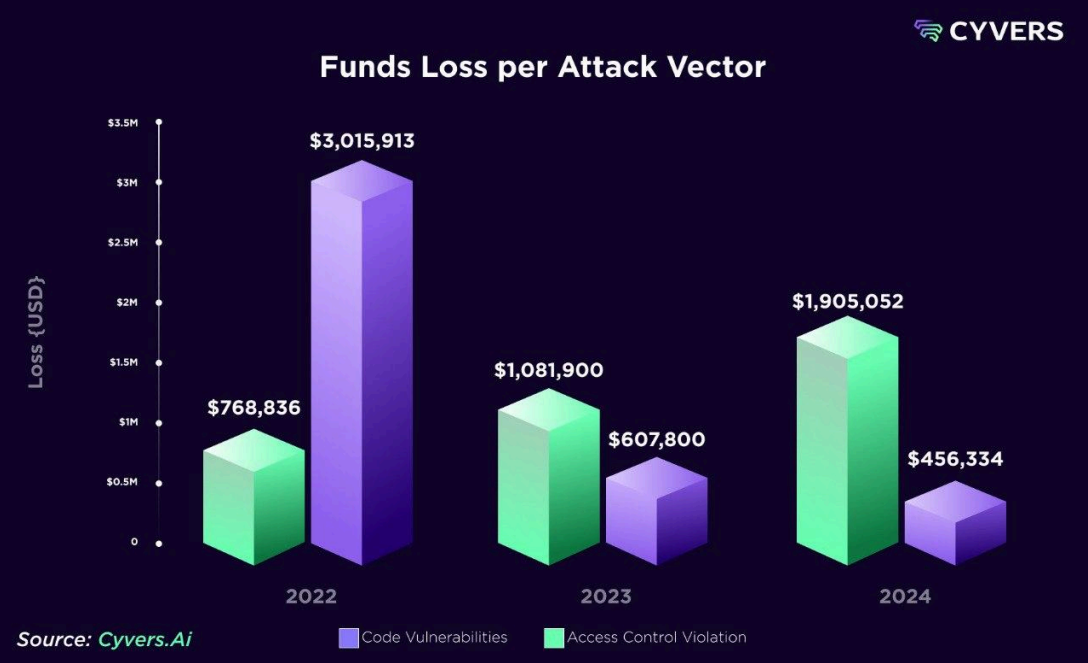
According to Cyvers’ annual report, access control vulnerabilities stand out as the main cause of losses, responsible for 81% of stolen funds.
Although these incidents accounted for only 41.6% of incidents, their large impact reflects the dangers of mismanaged security protocols. Ethereum was the hardest hit blockchain this year, recording more than $1.2 billion in losses.
A rather worrying trend this year is the popularity of “Pig Butchering” scams. These complex phishing schemes have swindled more than $3.6 billion from unknowing users, with most of the activity concentrated on the Ethereum blockchain.
“The rise of access control breaches and sophisticated scams like Pig Butchering underscores the importance of deploying risk assessment, transaction authentication, and anomaly detection tools. AI driven. Security needs to evolve to overcome increasingly complex and coordinated attacks,” Cyvers told TinTucBitcoin.
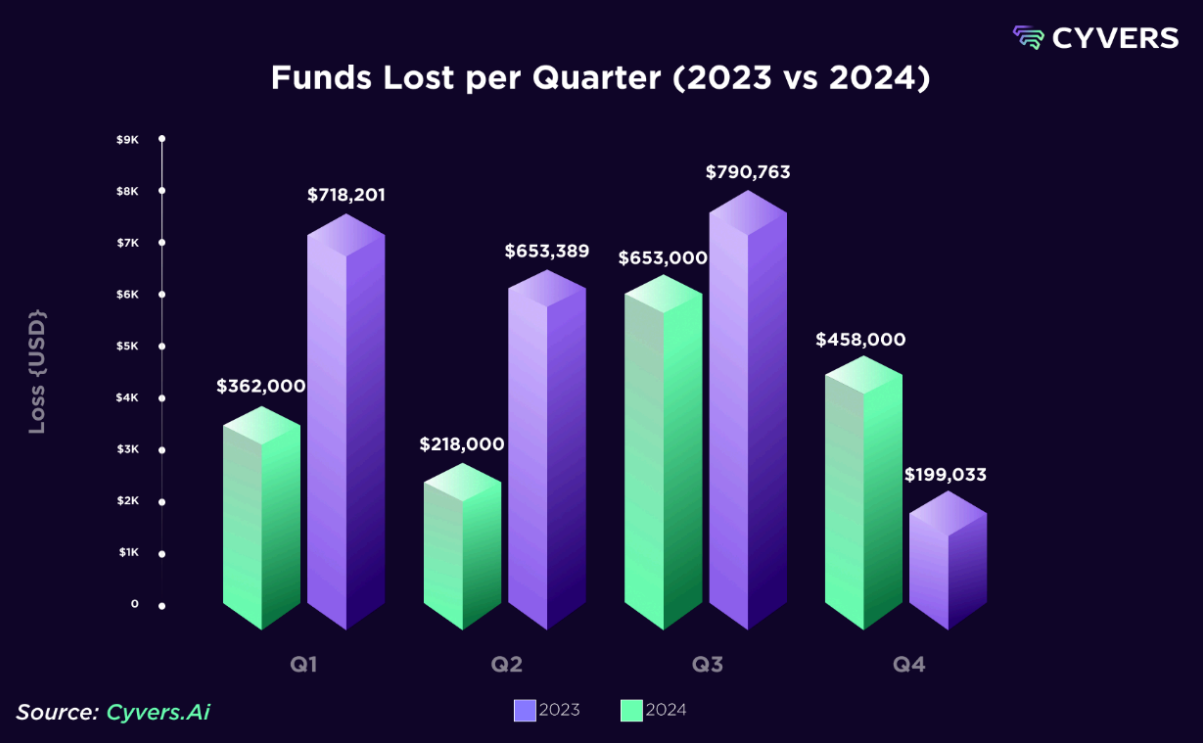
Furthermore, vulnerabilities in smart contracts also dominate the attack landscape, especially in DeFi. The third quarter of 2024 was the worst in terms of losses, with $790 million stolen during the period.
“If Cryptocurrency platforms do not want to become the next victim of hackers, they need to deploy robust detection and prevention systems and integrate them with their crisis response mechanisms. Cyvers data shows that 9 out of 10 hacked smart contracts have been audited and many of them have undergone rigorous penetration testing. Clearly, this is not enough,” Cyvers researchers noted.
In contrast, the fourth quarter recorded markedly lower activity, indicating a temporary lull in malicious activities.
The Biggest Cryptocurrency Hacks of 2024: WazirX, Radiant Capital, and DMM Bitcoin
The biggest individual incidents of the year have highlighted weaknesses in the Cryptocurrency ecosystem.
In July, Indian Cryptocurrency exchange WazirX suffered a devastating attack, losing approximately $234.9 million. Attackers exploited weaknesses in multisig electronic wallets, gaining unauthorized access to funds.
Multisig wallets, which require multiple private keys to approve transactions, are generally considered more secure. However, this incident has shown how poor implementation of these systems can lead to serious breaches.
WazirX has temporarily suspended trading and withdrawals for damage control and conducted a comprehensive security audit. Despite this effort, the exchange remains online except while seeking regulatory approval to resume operations.
“We are working to obtain court approval of the Plan as soon as feasible. Subject to legal and regulatory requirements, the platform will resume trading once effective from the date of implementation of the Plan,” WazirX recently said. write on X (formerly Twitter).
In November, Indian authorities arrested a suspect in connection with the hack, although the mastermind remained hidden. Investigators criticized Liminal Custody, the company responsible for securing WazirX’s digital wallets, for failing to provide key information during the investigation.
Radiant Capital, a prominent blockchain lender, was also a prominent victim this year. In October, the platform lost more than $50 million in a multi-chain attack.
Hackers are believed to have accessed three of the platform’s private keys, allowing them to dump assets across multiple networks, including Arbitrum, Binance Smart Chain, Base, and Ethereum.
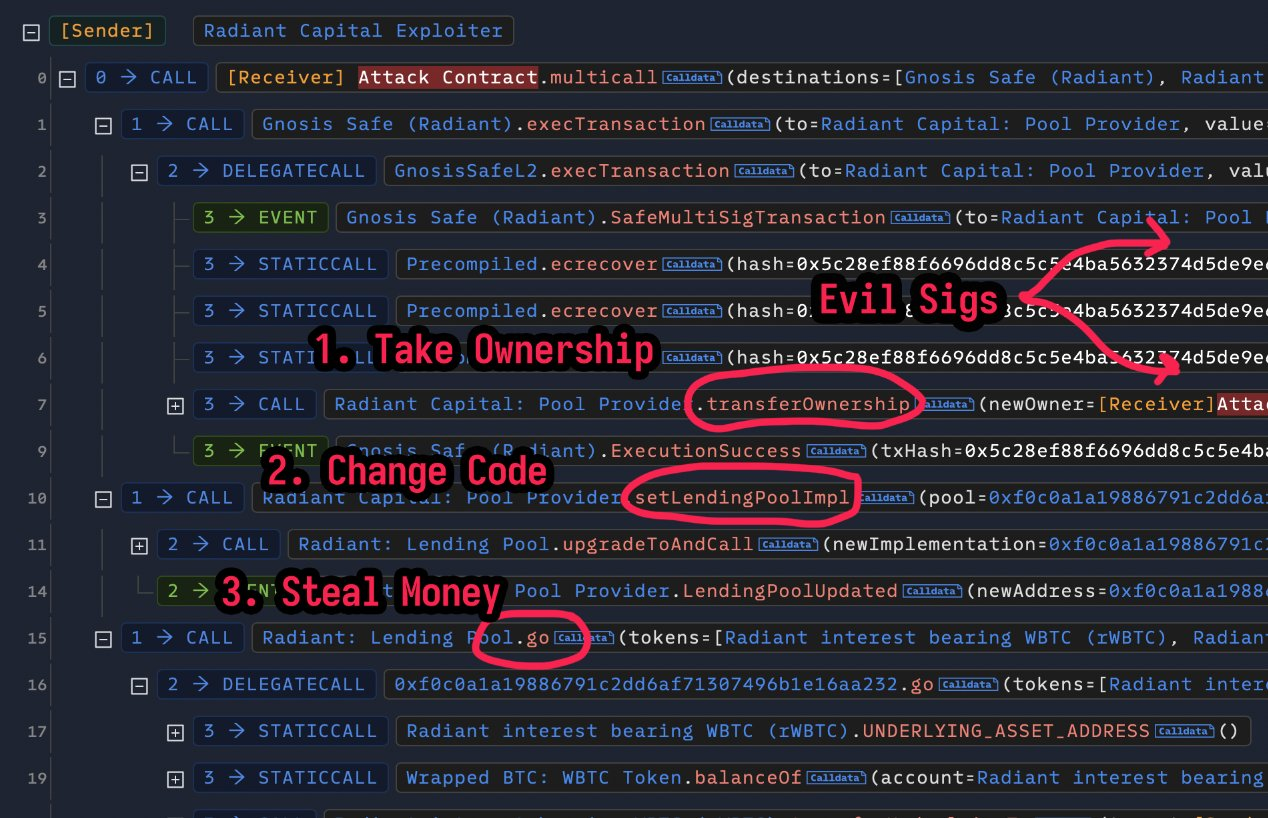
The attack has been attributed to North Korean-sponsored actors, who are increasingly targeting the Cryptocurrency industry with innovative tactics. The Radiant Capital hack reflects the heightened risks associated with multi-chain operations and the urgent need for better private key management.
Meanwhile, Japanese Cryptocurrency exchange DMM Bitcoin faced one of the most serious incidents of 2024. In May, the platform lost approximately 4,502.9 Bitcoin, worth $320 million at that point, after the attacker compromises a private key. Despite lengthy efforts to recover stolen assets and reassure customers, DMM Bitcoin announced its closure in December.
The exchange has started transferring user accounts to SBI VC Trade, marking a sad end to its operations. The incident highlights the devastating impact of insufficient key security, especially for centralized platforms.
Risk from CeFi and New Threats from Advanced Technology
Centralized finance (CeFi) platforms continue to face significant challenges. Single points of failure, such as centralized reserves and insufficient key management oversight, make these platforms attractive targets for attackers.
Reliance on multisig wallets, which have proven vulnerable under certain conditions, exacerbates this risk. Emerging technologies such as quantum computing and artificial intelligence are expected to further increase threats by enabling increasingly sophisticated attack methods.
These developments require proactive security measures to keep pace with the dynamic threat landscape. Experts have noted that incidents like the WazirX and Radiant Capital incidents could have been avoided if proactive threat monitoring solutions had been used.
“We can assess with confidence that notable attacks such as the $235 million WazirX hack and the $50 million Radiant Capital hack could have been avoided and that 100% of the funds could have been are kept safe if companies use such solutions,” Cyvers told TinTucBitcoin.
The sharp increase in malicious activity this year reflects the urgent need for stronger protections across the entire Cryptocurrency ecosystem. Platforms that lack real-time monitoring and preventative security tools remain extremely vulnerable to compromise, putting user funds at risk.
The industry must prioritize the adoption of advanced security measures and promote greater collaboration among stakeholders to effectively address ongoing threats.
“Zero-day attacks are unpredictable and are not based on known practices. Without real-time monitoring and detection mechanisms, as well as front-end tools — Cryptocurrency platforms cannot handle and prevent such attacks in real time,” say experts. Cyvers noted.
As the Cryptocurrency industry continues to grow, the creativity of attackers seeking to exploit weaknesses will also increase. Incidents this year have made it clear that reactive measures are no longer enough.
