What is Mempool?
The mempool is wherever all the unconfirmed transactions a node can see on the Bitcoin network.
Each node has the capability to retailer various unconfirmed transactions. Therefore, every single node has its very own edition of pending transactions. This explains the wide variety of sizes of Mempool.
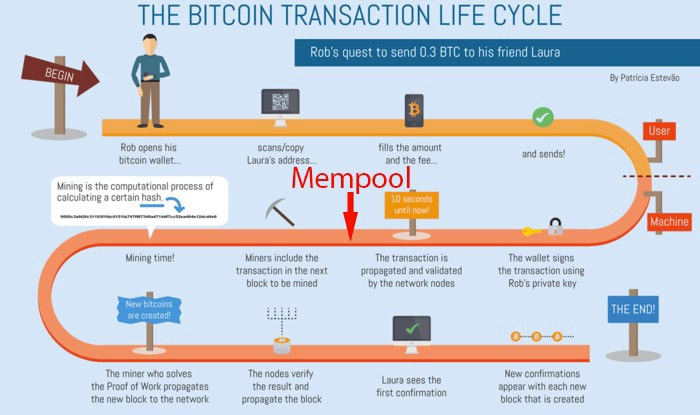
How does Mempool operate?
Bitcoin transactions are sent via a network of peer-to-peer connections, identified as nodes. Each node has its very own set of unconfirmed transactions sent by other linked peers. Nodes verify or invalidate transactions on a wide variety of criteria, which include right cryptographic signature, if the sum invested is double or if the input sum is better than the output sum.

Valid and invalid transactions are then transmitted to other neighboring nodes. Valid transactions are chosen by the mining nodes to be encapsulated in a block immediately after a enough quantity of nodes have propagated legitimate transactions across the network. Nodes clear away invalid transactions from their mempool when requested by their colleagues.
Mempools can be measured in various strategies, but are typically implemented in terms of fee per byte or satoshi per byte (sats / byte).
The website link involving Mempool and transaction costs
If we contemplate the mempool as a waiting area, when it is congested, there will be a higher sum of transactions waiting to be launched. Normally, transactions enter and depart the mempool smoothly when they are checked and extra to the block, but occasionally the mempool can turn out to be congested.
Periods of congestion can normally end result from a higher trading volume or a sudden drop in trade hash. During these occasions, the mempool turns into congested and delays can come about, resulting in elevated transaction costs.
The phrase “trade hash” refers to the issues of blockchain mining. There could not be adequate miners to deal with the complexity or congestion of the blockchain at that time. As a end result, some transactions have to wait longer to be confirmed.
Each Bitcoin transaction stays in the mempool until finally it is prepared to be confirmed, but there is no exceptional mempool. Each node has an related mempool and, by default, the mempool commonly does not exceed 300MB.
When the mempool is congested, consumers have the possibility to shell out increased costs, which can push their transactions up for more rapidly confirmations. Otherwise, transactions with reduced costs will stay in the mempool, wherever they will stay unconfirmed until finally the bottleneck is resolved. Likewise, all through intervals of minimum congestion when the volume of transactions is lower, the costs will be correspondingly reduced. Once a transaction has been chosen and extra to a confirmed block, that transaction is eliminated from the mempool.
summary
Above is the standard information and facts about the mempool summarized by Coinlive. Coinlive wishes you results and earn a great deal from this prospective market place.